Numpy is the most basic and a powerful package for working with data in python. Numpy provides the excellent ndarray objects, short for n-dimensional arrays.
Creating NumPy Arrays, Loading and Saving Files
Numpy is an external library, and that need to be install before you use it. After you installed, you have to import it every time you want to use it in your Python IDE.
To import NumPy you need to write the following code:
import numpy as np
Create Numpy Array:
arr1 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5], dtype=np.float64)
a.ndim, a.shape, a.size
np.zeros((3,4), 'd')
np.empty((4,4), 'd')
Some more stuff using Numpy:
# A Linspace Array is an array of equally spaced values going from a start to an end value.
# The NumPy linspace function in Python for creating numeric sequences over a specified interval.
np.linspace(0,10,5)
# The NumPy arange function returns evenly spaced numeric values within an interval, stored as a NumPy array.
np.arange(0,10,2)
np.random.rand(3,4) # Will create a 3x4 array of random numbers between 0 and 1
np.random.standard_normal((2,3))
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
b = np.array([[5,6],[7,8]])
# numpy.vstack() function is used to stack the sequence of input arrays vertically to make a single array.
np.vstack([a,b])
# numpy.hstack() function is used to stack the sequence of input arrays horizontally .
np.hstack([a,b])
# With the help of Numpy numpy.transpose(), We can perform the simple function of transpose within one line by using numpy.transpose() method of Numpy.
a.transpose()
Convert a List to Numpy array:

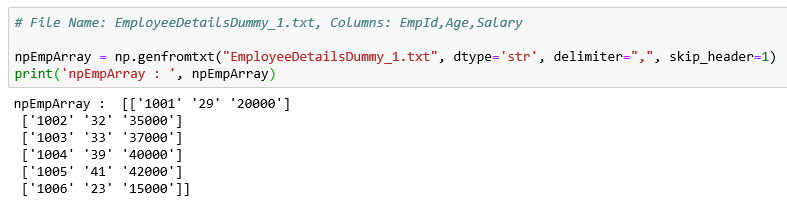
Fetching data from Text/CSV file into Numpy array using the np.genfromtxt() function:
npEmpArray = np.genfromtxt("EmployeeDetailsDummy_1.txt", dtype='str', delimiter=",", skip_header=1)
print('npEmpArray : ', npEmpArray)
You can also save NumPy arrays to files by using np.savetxt(). For example:
np.savetxt(‘file.txt’,arr,delimiter=’ ‘) #will save to a text file and
np.savetxt(‘file.csv’,arr,delimiter=’,’) #will save to a CSV file.
Indexing and Slicing
Indexing and slicing NumPy arrays works very similarly to working with Python lists: array[5] will return the element in the 5th index, and array[2,5] will return the element in index[2][5]. You can also select the first five elements, for example, by using a colon (:). array[0:5] will return the first five elements (index 0–4) and array[0:5,4] will return the first five elements in column 4. You can use array[:2] to get elements from the beginning until index 2 (not including index 2) or array[2:] to return from the 2nd index until the end of the array. array[:,1] will return the elements at index 1 on all rows.
Assigning values to a NumPy array is, again, very similar to doing so in Python lists: array[1]=4 will assign the value 4 to the element on index 1; you can do it to multiple values: array[1,5]=10 or use slicing when assigning values: array[:,10]=10 will change the entire 11th column to the value 10.
Sorting and Reshaping
array.sort() can be used to sort your NumPy array — you can pass different arguments inside the brackets to define what you want to sort on (by using the argument ‘order=string/list of strings’, for example. array.sort(axis=0) will sort specific axis of the array — rows or columns. two_d_arr.flatten() will flatten a 2 dimensional array to a 1 dimensional array. array.transpose() will transpose an array — meaning columns will become rows and vice versa. array.reshape(x,y)would reshape your array to the size you set with x and y. array.resize((x,y)) will change the array shape to x and y and fill new values with zeros.
Combining and Splitting
You can use np.concatenate((array1,array2),axis=0) to combine two NumPy arrays — this will add array 2 as rows to the end of array 1 while np.concatenate((array1,array2),axis=1) will add array 2 as columns to the end of array 1. np.split(array,2) will spilt the array into two sub-arrays and np.hsplit(array,5) will split the array horizontally on the 5th index.
Adding and Removing Elements
There are, of course, commands to add and remove elements from NumPy arrays:
np.append(array,values)will append values to end of array.np.insert(array, 3, values)will insert values into array before index 3np.delete(array, 4, axis=0)will delete row on index 4 of arraynp.delete(array, 5, axis=1)will delete column on index 5 of array
Descriptive Statistics
You can use NumPy methods to get descriptive statistics on NumPy arrays:
np.mean(array,axis=0)will return mean along specific axis (0 or 1)array.sum()will return the sum of the arrayarray.min()will return the minimum value of the arrayarray.max(axis=0)will return the maximum value of specific axisnp.var(array)will return the variance of the arraynp.std(array,axis=1)will return the standard deviation of specific axisarray.corrcoef()will return the correlation coefficient of the arraynumpy.median(array)will return the median of the array elements
Doing Math with NumPy
Any tutorial to NumPy would not be complete without the numerical and mathematical operations you can do with NumPy! Let’s go over them:
np.add(array ,1) will add 1 to each element in the array and np.add(array1,array2) will add array 2 to array 1. The same is true to np.subtract(), np.multiply(), np.divide() and np.power() — all these commands would work in exactly the same way as described above.
You can also get NumPy to return different values from the array, like:
np.sqrt(array)will return the square root of each element in the arraynp.sin(array)will return the sine of each element in the arraynp.log(array)will return the natural log of each element in the arraynp.abs(arr)will return the absolute value of each element in the arraynp.array_equal(arr1,arr2)will returnTrueif the arrays have the same elements and shape
It is possible to round different values in array: np.ceil(array) will round up to the nearest integer, np.floor(array) will round down to the nearest integer and np.round(array) will round to the nearest integer.
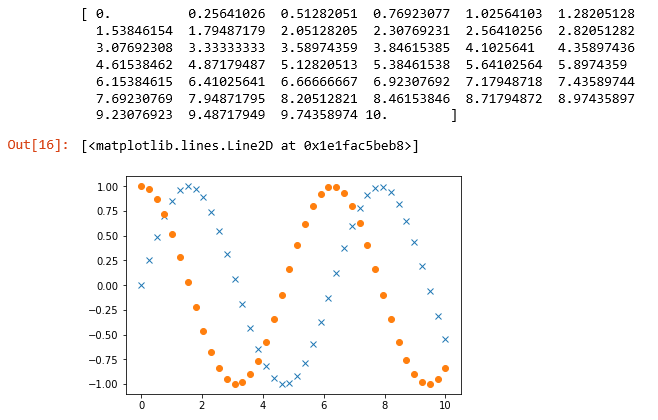
x = np.linspace(0,10, 40)
print(x)
sinx = np.sin(x)
cosx = np.cos(x)
pp.plot(x, sinx, 'x')
pp.plot(x, cosx, 'o')
Output:
Reference Source: A Quick Introduction to the NumPy Library by Adi Bronshtein

Leave a comment