Git: an open source, distributed version-control system. You can download git from here: https://git-scm.com/downloads
GitHub: a platform for hosting and collaborating on Git repositories.
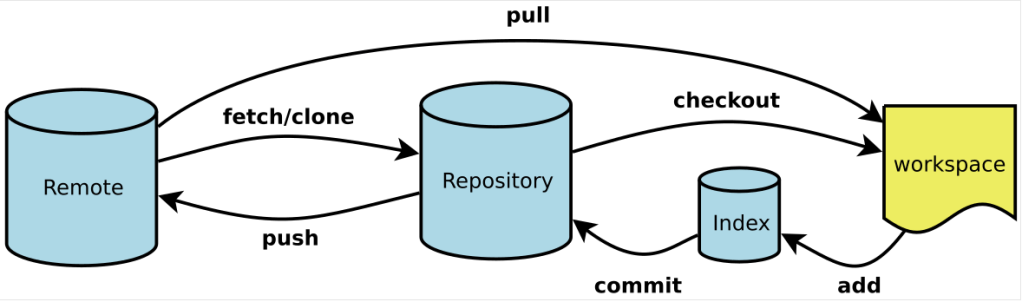
Basic Git commands
Open command window. Change your working directory.cd <working directory path>
Check your Git informationgit config --global --list
Create an empty Git repository or reinitialize an existing onegit init
Clone a Git repository into new directory.
Example of repository path:
- HTTPS: https://github.com/github-org/githubproject.git
- SSH: git@github.com:github-org/githubproject..git
git clone https://github.com/<user name>/<repository name>.git
Stage/Add all files which recently changed. Here “.” is for all files.git add .
Stage/Add specific file.git add <file path>
Commit your changes. Here the last parameters is your comments.git commit -m 'Initial commit.'
List all remote version.git remote -v
Push your code to specific remote and branch.git push https://github.com/<user name>/<repository name>.git master
Update your local branch from corresponding to your remote branch.git pull
Create a branch.git checkout -b
Working with an existing branch. Command for switching branch.git checkout
Git Cheatsheet
GIT is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
Install GIT:
●Install GIT for Windows
Download the latest version of GIT from https://git-scm.com/download/win
Follow the instructions on GIT setup wizard to complete the installation.
●Install GIT for Linux
$ sudo apt-get update
●To Install GIT from Command Window Using apt-get(Ubuntu/DebianDistribution)
$ sudo apt-get update
●To Install GIT for RPM-based distribution
$ sudo dnf install git-all
●Install GIT for Mac-OS
Download the latest version of GIT from https://git-scm.com/download/mac
Follow the instructions on Git setup wizard to complete the installation.
Configure Tooling:
GIT comes with a tool called git config that lets you get and set configuration variables that control all aspects of how Git looks and operates.
1.To View all of account settings:
$ git config --list --show-origin
-Git is to set your user name and email address. This is important because every Git commit uses this information, and it’s immutably baked into the commits you start creating.
-To use Git we need to attach username and email to commit any transactions
2.To set Username:
$ git config --global user.name "abc"
3.To set Email:
$ git config --global user.email abc@xyz.com
4.To set main as the default branch:
$ git config --global init.defaultBranch main
5.To check the configuration settings use:
$ git config --list
6.To get help for Config:
$ git help config
Create Repositories:
There are two methods to obtain a Git repository:
1.You can take a local directory that is currently not under version control, and turn it into a Git repository.
2.You can clone an existing Git repository from elsewhere.
●To turn a directory into a Git repository:
$ git init
●To clone a existing repository located at [url]:
$ git clone [url]
GIT Branching:
Branch operation allows creating another line of development
●To Create a new branch:
$ git branch [branch_name]
●To checkout a new branch named [branch_name]:
$ git checkout [branch_name]
●To delete an existing branch:
$ git branch -d [branch_name]
●To merge specific branch to current branch:
$ git merge [branch]

Leave a comment